If you are not already a subscriber, you are welcome to enter your email address here to sign up to receive the Space History newsletter on a daily basis. Under no circumstances will we release your legitimate email address entered here to outside persons or organizations, and it will only be used for mailing the specific information you have requested.
| Enter your email address here: |
Unsubscribe instructions are included in every newsletter issue in case you decide you no longer wish to receive it.
Note: We record the IP address from which subscriptions are entered to help prevent SPAM abuses.
Race To Space
Someone will win the prize...
... but at what cost?
Visit RaceToSpaceProject.com
to find out more!
1826
Died, Johann Bode, German astronomer, reformulated and popularized the Titius-Bode Law stating the relationship between planetary orbits
ref: en.wikipedia.org
1837
Born, John van der Waals (at Leyden, the Netherlands), physicist, Nobel 1910 "for his work on the equation of state for gases and liquids"
ref: www.nobelprize.org
1864
Died, Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, astronomer (double stars)
ref: en.wikipedia.org
1867
R. Luther discovered asteroid #95 Arethusa.
1868
Louis Ducos du Hauron patented a trichrome color photo process in France.
Arthur-louis Ducos Du Hauron (8 December 1837 - 30 August 1920) was a French physicist and inventor who developed the trichrome process of color photography in 1869, a key 19th century contribution to photography.
Louis Ducos du Hauron began experimenting in his twenties. On 1 March 1864, he patented a device for taking and projecting motion pictures, but did not build it. Four years later, on 23 November 1868, he patented a process for making color photographs. The French patent (nr. 83061) was granted 23 February 1869. Using his process, he photographed a scene through green, orange, and violet filters. The three negatives were then printed on thin sheets of bichromated gelatin containing carbon pigments of red, blue, and yellow, the complementary colors of the negatives. When the three positive transparencies were superimposed, a full-color photograph resulted. Another French experimenter, Charles Cros, discovered the process independently, publishing his findings just 48 hours after Ducos du Hauron received his patent. Ducos du Hauron described his results in two books - "Les Couleurs en photographie: Solution du probleme" ("Colours in Photography: Solution of the Problem", 1869) and "Les Couleurs en photographie et en particulier l'heliochromie au charbon" ("Colours in Photography: Colour Reproduction with Carbon Pigments", 1870).
Ducos du Hauron continued his research, devising improvements and cost reductions for printed color reproductions. In 1891 he also patented the anaglyph, a type of three-dimensional photography that uses colored filters to superimpose separate images for the left and right eyes on one picture.
Ducos du Hauron did not profit much from his inventions, but he did receive a pension from the government, and was made a chevalier of the French Legion of Honor in 1912.
ref: books.google.com
1892
A. Charlois discovered asteroid #345 Tercidina.
1897
A. Charlois discovered asteroid #429 Lotis.
1921
A. Schaumasse discovered asteroid #971 Alsatia.
1922
G. Van Biesbroeck discovered asteroid #990 Yerkes.
1935
Born, Vladislav Volkov (at Moscow, Russian SFSR), Soviet cosmonaut (Soyuz 7, Soyuz 11/Salyut 1; over 28d 17h total time in spaceflight), member of first crew to stay aboard a space station (Salyut 1) (deceased)
Vladislav Nikolayevich Volkov (23 November 1935, Moscow - 29 June 1971) was a Soviet cosmonaut who flew on the Soyuz 7 and Soyuz 11 missions. Soyuz 11 docked with Salyut 1 on 7 June 1971, the first space station flight in history.
Volkov had the unfortunate distinction of being part of the second crew to die during a space flight: After a normal re-entry, the Soyuz 11 capsule was opened and the crew was found dead. It was discovered that a valve had opened just prior to leaving orbit that had allowed the capsule's atmosphere to vent away into space, suffocating the crew.
ref: en.wikipedia.org
ref: www.spacefacts.de
1936
K. Reinmuth discovered asteroids #1408 Trusanda and #1435 Garlena.
1948
Frank G. Back received a patent for a "varifocal lens for cameras" that provides "zoom" effects. Variable focus lenses such as this enable spacecraft cameras to take both wide angle and telephoto shots without changing lenses.
ref: patents.google.com
1948
M. Laugier discovered asteroid #1681 Steinmetz.
1949
L. Boyer discovered asteroid #1594 Danjon.
1960 11:13:00 GMT
NASA launched TIROS 2 (Television and InfraRed Observation Satellite) on a Thor-Delta from Cape Canaveral, Florida, a spin-stabilized meteorological spacecraft designed to test experimental television techniques and infrared equipment.
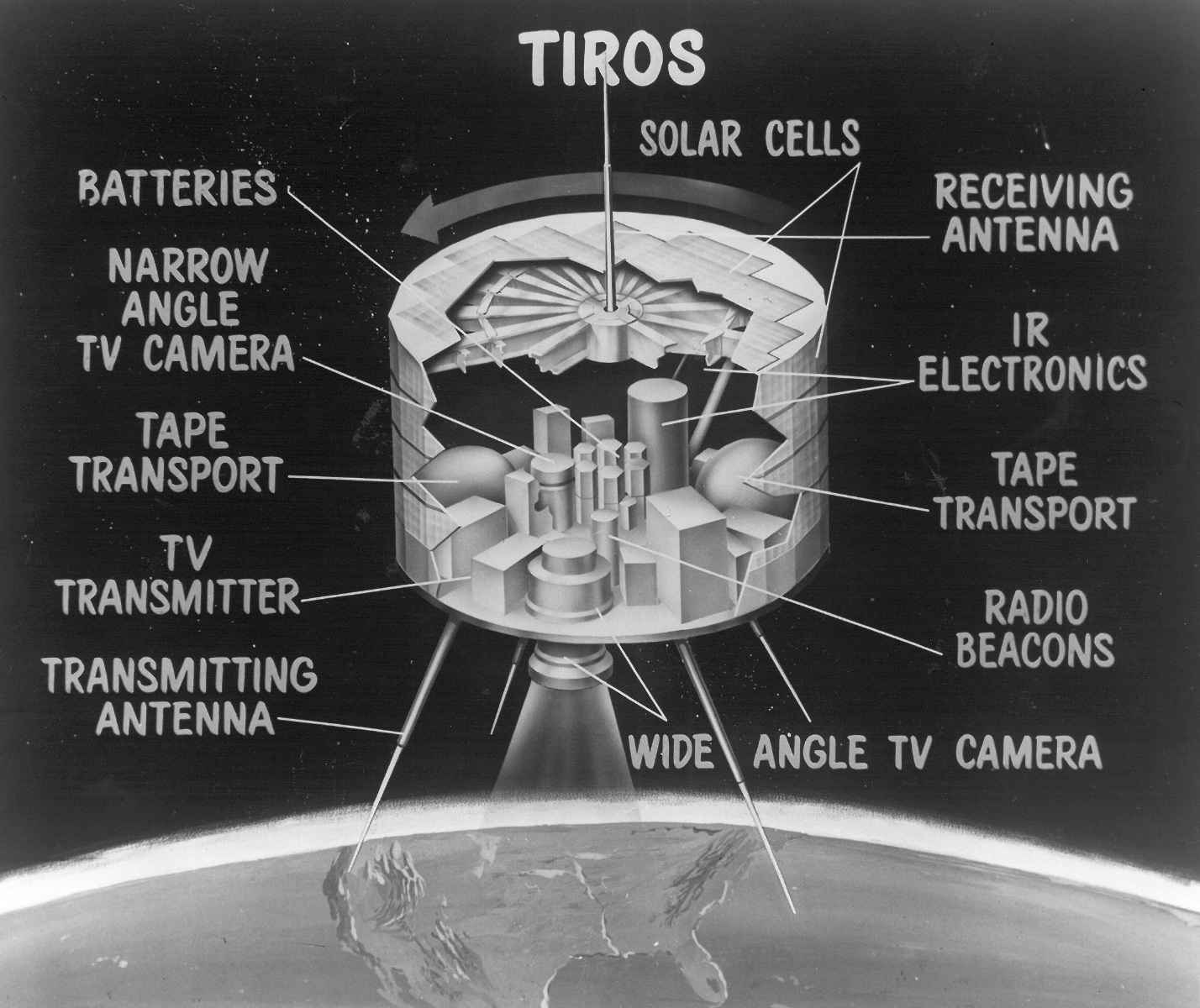
TIROS satellite instrumentation, NASA illustration
ref: nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov
1977 01:35:00 GMT
The European weather satellite Meteosat 1 was launched on a Delta rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida, as part of European Space Agency's (ESA) contribution to the Global Atmospheric Research Program (GARP).
ref: nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov
1983 19:58:00 GMT
USSR Soyuz T-9 landed, returning cosmonauts V. A. Lyakhov and A. P. Aleksandrov from the Salyut 7 space station.
ref: nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov
2002 18:50:00 CST (GMT -6:00:00)
NASA launched STS 113 (Endeavour 19, Shuttle 112, ISS Flight 11A) to deliver a new crew and truss segment to the International Space Station.
STS 113 was launched 23 November 2002, the 16th shuttle mission to the International Space Station (designated ISS Flight 11A). Orbit insertion altitude: 122 nautical miles. Orbit inclination: 51.60 degrees. During its 14 day mission, the STS 113 crew extended the International Space Station's backbone with installation of the P1 (P-One) Truss, and exchanged the Expedition Five and Six crews. About 1,969 kilograms (4,340 pounds) of cargo were transferred between the shuttle and station. Endeavour docked with the station 25 November and undocked on 2 December. Three EVAs were conducted. The mission ended on 7 December 2002 when Endeavour landed at Kennedy Space Center, Florida. Mission duration: 13 days, 18 hours, 47 minutes. The landing was the first time a mission ended on the fourth day of landing attempts.
See also NSSDCA Master Catalog
ref: www.nasa.gov
We are going to run out of oil!
Visit SpacePowerNow.org
to help fix the problem.
SpacePowerNow.org - For Human Survival
Please help support our efforts by shopping from our sponsors.
This newsletter and its contents are Copyright © 2006-2026 by The L5 Development Group. All rights reserved. - Publication, in part or in whole, requires previous written permission. - Academic or personal-use citations must refer to http://L5Development.com as their source. Thank you for your cooperation.
Space History Department
Resources
The L5 Development Group Home Page
The L5 Development Group Keyword Access System
Space History for November 23 /
Webmaster /
Script last modified August 23, 2018 @ 6:05 am
Copyright © 2006-2026 by The L5 Development Group. All rights reserved.
Hosted by FKEinternet






